Industrial Chemicals
324 products.
Filter by Application
[Close]
76 products.
[Close all]
High Purity Ethylene Carbonate
[Close]
High Purity Ethylene Carbonate. As ethylene carbonate is a highly polar solvent and dissolves large amount of electrolyte, it is mainly used in lithium batteries electrolyte solution. It can also readily dissolve polymers leading to use as a release agent and detergent. Our product is high quality with low impurity levels and low moisture. It has earned an excellent reputation for adherence to the strict quality standards demanded by our customers.
EINECS: No.202-510-0
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 5-523
Triethylene glycol
[Close]
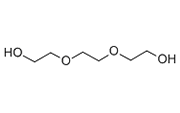
Triethylene Glycol is widely used as a solvent. It has a high flash point, emits no toxic vapors, and is not absorbed through the skin.
EINECS: No. 203-953-2
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-429
Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.3 (water soluble liquid).
Diethylene glycol
[Close]
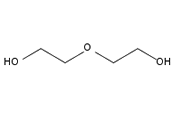
Diethylene glycol is widely used as a solvent. It has a high flash point, emits no toxic vapors, and is not absorbed through the skin.
EINECS: No. 203-872-2
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-415
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.3(water soluble liquid).
Ethylene glycol
[Close]
Monoethylene glycol is one of the main raw materials for polyethylene terephthalate (PET resin). It is widely used for automotive antifreeze solutions because the freezing point is low, toxicity is low, and it is completely miscible in water.
EINECS: No. 203-473-3
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-230
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 3 (water-soluble liquid).
Ethylene Carbonate
[Close]
As ethylene carbonate is a highly polar solvent and dissolves large amount of electrolyte, it is mainly used in lithium batteries electrolyte solution. It can also readily dissolve polymers leading to use as a release agent and detergent. Our product is high quality with low impurity levels and low moisture. It has earned an excellent reputation for adherence to the strict quality standards demanded by our customers.
EINECS: No.202-510-0
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 5-523
2-Ethyl hexanol
[Close]
2-Ethyl hexanol is an 8-carbon higher alcohol species. It is used to make the vinyl chloride plasticizer, bis(2-ethyl hexyl) phthalate. It is also used to make 2-ethyl hexyl acrylate for adhesives and paints.
EINECS: No. 203-234-3
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-217
Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class4 Petroleums No.3 (non-water soluble liquid).
n-Butanol
[Close]
Normal butanol is a 4-carbon, straight-chain alcohol. It is used as a solvent and as a raw material for coating resins, butyl acrylate, butyl acetates, glycol ethers, etc.
EINECS: No. 200-751-6 Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-3049
Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
Japan Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.2 (non-water soluble liquid).
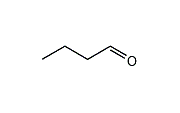
n-Butyraldehyde
[Close]
Isobutanol
[Close]
Isobutanol is a 4-carbon branched-chain alcohol used as a raw material for coating resins, Isobutyl acrylate, isobutyl acetate, isobutyl methacrylate, and paint thinners.
(CH3)2CHCH2OHO
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-3049
Japan, Industrial Safety and Health Law: No. 2-3049
Japan, Law for Pollutant Release and Transfer Register: Not applicable.
Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
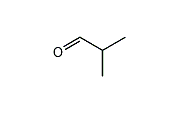
Isobutyraldehyde
[Close]
Methyl Acrylate
[Close]
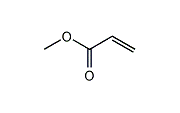
Methyl acrylate is the ester of acrylic acid and methanol. It is a raw material for applications including acrylic fibers, molding resins, adhesives, coatings, and emulsions.
EINECS: No. 202-500-6
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-987
Japan,Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 1 (non-water soluble liquid).
Butyl Acrylate
[Close]
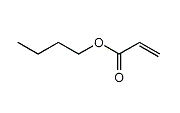
Butyl acrylate (BA) is the ester of acrylic acid and n-butanol. It is used as a raw material for fiber processing agents, adhesives, coatings, plastics, acrylic rubber, and emulsions.
EINECS: No. 205-480-7
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-989
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 2 (non-water soluble liquid).
Ethyl Acrylate
[Close]
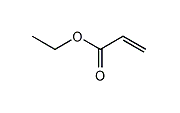
Ethyl Acrylate (EA) is the ester of acrylic acid and ethanol. It is used as a raw material for fiber processing agents, adhesives, coatings, plastics, acrylic rubber, and emulsions.
EINECS: No. 205-438-8
Japan Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-988
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 1 (non-water soluble liquid).
Isobutyl Acrylate
[Close]
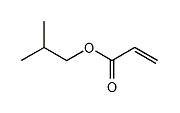
Isobutyl Acrylate (IBA) is the ester of acrylic acid and isobutyl alcohol. It is used as a raw material for adhesives, coatings, plastics, and emulsions.
EINECS: No. 203-417-8
Japan Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-989
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 2 (non-water soluble liquid).
2-Ethylhexyl acrylate
[Close]
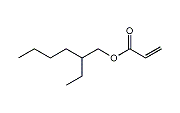
2-Ethylhexyl acrylate (HA) is the ester of acrylic acid and 2-ethyl hexanol. It is used as a raw material to make adhesives, coatings, construction materials, acrylic rubber, and emulsions.
EINECS: No. 203-080-7
Japan Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-990
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 3 (non-water soluble liquid).
Acrylic Acid・Toluene
[Close]
Acrylic acid is made by the direct oxidation of propylene. Acrylic Acid・Toluene is made by diluting acrylic acid with toluene in a 7:3 ratio.
Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Hazardous substance
Phenol
[Close]
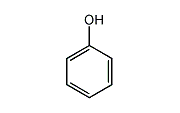
Phenol is an aromatic hydrocarbon compound composed of a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group. It is used as a raw material to make phenolic resins, bisphenol A for epoxy resins, and various pharmaceuticals.
- EINECS: No. 203-632-7
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 3-481
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law: Designated combustibles (flammable solid)
Bisphenol A (BPA)
[Close]
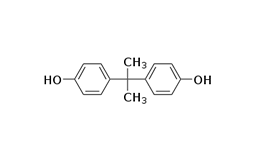
Bisphenol A is produced by reaction of phenol with acetone, and is used as a raw material and additive for epoxy resins and plastics. Mitsubishi Chemical's bisphenol A purity is a major advantage.
- EINECS: No. 201-245-8
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 4-123
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law: Not applicable.
Cumene
[Close]
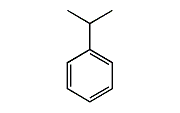
Cumene is an aromatic hydrocarbon used as a raw material for the production of phenol and acetone by the cumene method. Mitsubishi Chemical's cumene features high purity.
- EINECS: No. 202-704-5
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 3-22
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.2 (non-water soluble liquid).
alpha-Methylstyrene is similar to styrene in its polymerization, but if it is used instead of styrene to make ABS resin, the ABS resin will have better thermal stability. alpha-Methylstyrene is also used as a raw material for paints and adhesives.
- EINECS: No. 202-705-0
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: No. 3-5
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.2 (non-water-soluble liquid).

BioPTMG is a polyether polyol manufactured from plant-derived raw materials.
BioPTMG has the same performance as petroleum-derived PTMG as a raw material for polyurethane and polyester resins and has excellent impact, wear and hydrolysis resistance, flexibility at low temperatures, etc. Taking advantage of these characteristics, it can be used in a wide range of fields, from interior and fashion to industrial materials.
- Grades:
- BioPTMG650、BioPTMG1000、BioPTMG2000、BioPTMG3000
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law:
- (7)-129
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law:
- Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law:
- Hazardous Material Class 4 Petroleums No.4 Hazardous Rank III(BioPTMG650)
Combustible Materials, Flammable Solids(BioPTMG1000, 2000, 3000)
PTMG (Poly(tetramethylene ether)glycol / PTMG) is a linear polyether glycol with hydroxyl groups on both ends. As a polyol, it reacts readily with isocyanates (for example MDI, TDI), etc. to make resins with excellent properties.
- Grades:
- PTMG250、PTMG650、PTMG850、PTMG1000、PTMG1300、PTMG1500、PTMG1800、PTMG2000、PTMG3000、PTMG3200(developed grade in mass production)
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law:
- METI-No. 7-129
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law:
- Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law:
- Hazardous Material Class 4 Petroleums No.3 Hazardous Rank III (PTMG250)
Hazardous Material Class 4 Petroleums No.4 Hazardous Rank III (PTMG650,850)
Combustible Materials, Flammable Solids (PTMG1000, 1300, 1500, 1800, 2000, 3000, 3200(developed grade in mass production))
12BG (1,2-butanediol) is a branched glycol that has a primary hydroxyl group and a secondary hydroxyl group on adjacent carbon atoms. Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation offers two grades of purity. Both can be reacted with a dicarboxylic acid (e.g., phthalic acid or adipic acid) for use as a polyester polyol or a plasticizer, or reacted with an unsaturated dicarboxylic acid (e.g., maleic anhydride) for use as a raw material for unsaturated polyester resin. The high-purity grade 12BG is suitable for use as a solvent for inks and as a raw material for surfactants.
- EINECS: No. 209-527-2
- Chemical Substance Control Law (CSCL): METI-No. 2-235
- Japan, Industrial Safety and Health Act (ISHA): No. 2-235
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Service Act:Hazardous Materials, Category IV—Class III petroleums (water soluble liquids)
14BG (1,4-Butanediol) is a straight chain glycol with hydroxyl groups on both ends. It is used as a raw material for high performance polyester and polyurethane resins as well as for industrial chemicals like tetrahydrofuran and gamma-butyrolactone. Since 1982, Mitsubishi Chemical's Tokai plant has produced high-purity, high-quality 14BG from butadiene using our proprietary technology.
- EINECS: No. 203-786-5
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-235
- Japan, Industrial Safety and Health Law: No. 2-235
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.3 (water-soluble liquid).
Polycarbonatediol, BENEBiOL™
[Close]

Polycarbonatediol(PCD) is a linear polycarbonate with hydroxyl groups at both ends. It easily reacts with isocyanate compounds(e.g. MDI, TDI, IPDI, H12MDI), and generates polymers with characteristics such as durability and chemical/hydrolysis resistance. BENEBiOL™ is the biomass-based PCD developed by our proprietary manufacturing technology. Because of “key monomer“ of each grade, polyurethane resins based on BENEBiOL™ will show an outstanding property level with regard to flexibility and chemical/stain resistance for example, in addition to the characteristics of conventional PCD. Besides, your product will be equipped with unique touch and feeling.Biomass-based polycarbonatediol with superior characteristics
Characteristics of polyurethane resins based on BENEBiOL™
non-edible raw material is used for some grades
transparency, stain resistance, chemical resistance, durability, toughness, weather resistance
flexibility, soft feel and touch, high hardness, good fit
Available Technology Licenses
[Close]
MKC™ Silicate is an oligomer formed by the partial hydrolysis of tetramethoxysilane. As an additive in paints, it produces a hydrophilic surface that is highly stain-resistant with the self-cleaning effect.
YOSHINOX BB is a phenolic antioxidant used as a resin additive or resin chemical.
YOSHINOX 425 (2,2'-Methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol)) is a phenolic antioxidant used as a resin additive or resin chemical.
Tomirac KN is a high heat-resistant developer for thermal paper.
Vinyl acetate monomer (VAM)
[Close]
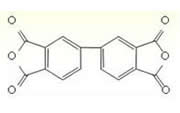
BPDA (3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride) is a raw material for the polyimide resin component of one of the super-engineering plastics. It is used for many important information and electronic technology products such as mobile phones and copying machines.
EINECS: No.219-342-9
Japan Chemical Mfg. Reg.: No.4-833
Japan Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable
Fire Services Law: Not applicable
Terephthalate Plasticizer
[Close]
Phthalate Plasticizers
[Close]
Adipate Plasticizer
[Close]
Other Plasticizers
[Close]
- Product Finder
-