Monoethylene glycol is one of the main raw materials for polyethylene terephthalate (PET resin). It is widely used for automotive antifreeze solutions because the freezing point is low, toxicity is low, and it is completely miscible in water.
EINECS: No. 203-473-3
Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 2-230
Japan, Fire Services Law: Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No. 3 (water-soluble liquid).
Characteristics
[Close]
Ethylene glycol is viscous at room temperature. It is colorless, odorless, and sweet-tasting. It is miscible in water in all ratios.
| Common Names | Monoethylene glycol, ethylene glycol |
|---|---|
| EINECES |
203-473-3 |
| Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law |
2-230 |
| Japan, Fire Services Law |
Hazardous material Class 4 Petroleums No.3 (water-soluble liquid). |
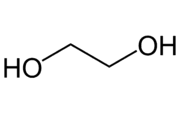
| Formula |
C2H6O2 |
| Structure |  |
| Flash Point (℃) |
120 (airtight) |
| Autoignition Temperature (℃) |
404 |
| Melting Point (℃) |
-13 |
| Boiling Point (℃) |
197.6 |
| Flammability Range (vol%) |
3.2~15.3 |
Applications
[Close]
Polyethylene terephthalate, polyester, PET bottles, antifreeze solutions
Usage Regulations
[Close]
Applicable Laws: Japan, Fire Service Law
Available volume specifications
[Close]
Tanker truckload (lorry), drum, oil can, ship (bulk).
Inquiries Concerning Products
View the products of C2 Chemicals Dept., Mitsubishi Chemical[Open in a new window]
