- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Ion Exchange Resin Business Gr. Separation Materials Dept.
Storngly Basic Anion Exchange ResinsDIAION™ series
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation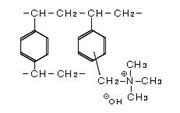
An amino functional group is incorporated into the anion exchange resin enabling the exchange of anions like the Cl- ion and the SO4-- ion. Strongly basic anion exchange resins and weakly basic anion exchange resins can be defined according to the basic strength of the amino functional group.
The ion exchange resin that has a quaternary ammonium group is strongly alkaline and dissociates just like NaOH and KOH. Therefore it is called a strongly basic anion exchange resin.
Characteristics
[Close]
The strongly basic anion exchange resin is an anion exchange resin with quaternary ammonium groups incorporated into the styrene frame. Two types with differing alkalinity strengths are: Type I with a trimethyl ammonium group, and Type II with a dimethylethanol ammonium group.
The strongly basic resin is used to produce high purity demineralized water, making use of the capability to strongly adsorb anions.
Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resin Chemical Structures
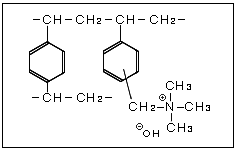
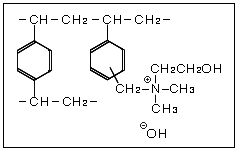
The strongly basic anion exchange resin's functional group behaves as a strong base making it possible to use the resin across the full pH range 0-14.
The following reactions show that the resin can carry out ion exchange not just with a mineral acid, but also with a salt like NaCl. In addition, the resin can carry out exchange capture of weak acids in solution such as silicic acid (aqueous silica) and carbonic acid.
R-N・OH + NaCl → R-N・Cl + NaOH
R-N・OH + HCl → R-N・Cl + H2O
R-N・OH + SiO2 → R-N・HSiO3
(R represents the ion exchange resin matrix.)
Regeneration of the strongly basic anion exchange resin is usually performed with about 4% NaOH solution. It cannot practically be regenerated with a weak base like NH4OH.
The reactions below show the regeneration of a strongly basic anion exchange resin that was previously loaded with Cl- ions.
R-N・Cl + NaOH → R-N・OH + NaCl
As with the strongly acidic cation exchange resin, it is relatively difficult to regenerate the strongly basic anion exchange resin. For practical purposes, the required amount of regenerant solution is several times the theoretical chemical equivalent.
Applications
[Close]
Applications include water treatment as well as purification of pharmaceuticals and food.
Usage
Packed column or Batch processing
Lineup / Specifications
[Close]
Mitsubishi Chemical's Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resins are listed below.
These styrene-based resins use quaternary ammonium groups for the exchange groups. Two types with differing alkalinity strengths are: Type I with a trimethyl ammonium group, and Type II with a dimethylethanol ammonium group.
There are the gel type SA series, the porous PA series, and the highly porous HPA25 (Type I) versions. The ionic form of the standard products is the Cl- form.
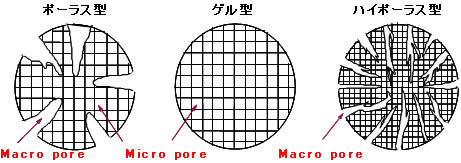
- Gel Type DIAION™ SA10 Series (Type I) and SA20 Series (Type II)
- Porous-Type DIAION™ PA300 Series (Type I)
- Highly Porous-Type DIAION™ HPA25L (Type I)
- Porous Type DIAION™ PA400 Series (Type II)
- Gel Type DIAION™ UBA Series
Refer to the "ION EXCHANGE RESINS "[別窓表示] websites for more details.
Inquiries Concerning Products
View the products of Separation Materials Dept., Mitsubishi Chemical[Open in a new window]
