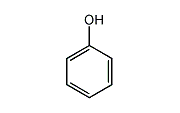
Phenol is an aromatic hydrocarbon compound composed of a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group. It is used as a raw material to make phenolic resins, bisphenol A for epoxy resins, and various pharmaceuticals.
- EINECS: No. 203-632-7
- Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law: METI-No. 3-481
- Japan, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law: Not applicable.
- Japan, Fire Services Law: Designated combustibles (flammable solid)
Characteristics
[Close]
Phenol is an aromatic hydrocarbon compound composed of a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group. At room temperature, it is a solid and has a characteristic chemical smell. The general physical properties are as follows.
| Common Names | Phenol Carbolic acid, Oxybenzene |
|---|---|
| Structure | 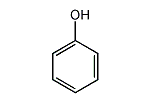 |
| Japan, Chemical Substances Control Law METI-No. | 3-481 |
| Formula | C6H5OH |
| Molecular Weight | 94 |
| Appearance | Colorless or white solid |
| Melting Point (℃) | 41 |
| Boiling Point (℃) | 182 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.07 |
| Flash Point (℃) | 79 |
| Autoignition Temperature (℃) | 715 |
| Flammability Range (%) | 1.8~8.6 |
| Solubility parameter | 14.5 |
Applications
[Close]
It is used as a raw material to make phenolic resins and bisphenol A which in turn is a raw material for epoxy resins. It is also used as a raw material for a variety of dyes, surfactants, disinfectants, agricultural chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and intermediate chemicals.
Inquiries Concerning Products
View the products of PHL & PC Dept., Mitsubishi Chemical[Open in a new window]
