- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Ion Exchange Resin Business Gr. Separation Materials Dept.
Characteristics
[Close]
Chelating resins
In contrast to an ion exchange resin, the chelating resin catches a metal ion with a functional group that can form a chelate (complex) with the metal ion.
The chelating resin makes use of the general principle that two or more electron donor elements such as N, S, O, and P are needed for chelation. Examples include N-O type, S-N type, N-N type, O-O type, etc., and the well-known iminodiacetic acid group [-N(CH2COO-)2] and polyamine group [-NH(CH2CH2NH)n・H].
In the DIAION™ CR Series, there are three product types: (1) for common metals -- DIAION™ CR11 with the iminodiacetic acid functional group, (2) for metals other than alkali metals (Na, K, etc.) or alkaline earth metals (Ca, Mg, etc.) -- DIAION™ CR20 with the polyamine group. The chemical structures of the resins and the chelates are shown below. In these structures, R represents the resin matrix which is polystyrene cross-linked with divinylbenzene.
- (1) DIAION™ CR11 Chemical Structure and Chelation Reaction
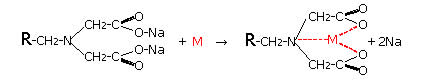
- (2)DIAION™ CR20 Chemical Structure and Chelation Reaction
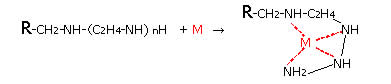
Compared to ion exchange resins, chelating resins feature very much greater selectivity for specific metal ions. For example, in a saturated brine solution, CR11 can reduce Ca, Mg, and Sr from ppm to ppb levels. With an ion exchange resin, it is not possible to capture Ca, Mg, and Sr like this with Na present at hundreds of thousands times higher concentration (even though Ca, Mg, and Sr nominally have higher selectivity on the ion exchange resin.)
When it is time to regenrate the chelating resin, acids like hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid are usually used to desorb the adsorbed metal ions. This utilizes the fact that these metal chelates are less stable at low pH and are more readily decomposed. However, there are cases in which regeneration is difficult; for example with CR11 or CR20 and valence 3 metal ions and Hg the selectivity is extremely strong, and a large quantity of regenerant solution may be required. In addition, some metal ions form complex salts in Hydrochloric acid solution, and regeneration in that case may not work well. In these cases, sulfuric acid is usually used as the regeneration solution.
The selectivity for various metal ions with CR11 and CR20 are shown below.
CR11
Cr3+ > In3+ > Fe3+ > Ce3+ > Al3+ > La3+ > Hg2+ > UO2+ > Cu2+ > VO2+ > Pb2+ > Ni2+ > Cd2+ > Zn2+ > Co2+ > Fe2+ > Mn2+ > Be2+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Sr2+
CR20
Hg2+ > Fe3+ > Cu2+ > Zn2+ > Cd2+ > Ni2+ > Co2+ > Ag+ > Mn2+
(K、Na、Li、Rb、Cs、Ca、Mg、Ba、Sr、Sn、Zr、Th、Al、Fe2+ are not captured)
Applications
[Close]
Applications include brine purification, chemical purification, wastewater treatment, and boric acid removal.
Usage
Packed column or Batch processing
Lineup / Specifications
[Close]
Metal ion capture by chelation has much higher selectivity than with strongly acidic or weakly acidic ion exchange resins. As metal valence increases, selectivity increases.
- CR11 Iminodiacetic Acid Type
It is widely used for heavy metal ion removal. - CR20 Polyamine Type
It has high selectivity for heavy metal ions, but does not capture alkali metal and alkaline earth metal ions.
Please see "ION EXCHANGE RESINS "[別窓表示]websites for more information about properties of each type.
Inquiries Concerning Products
View the products of Separation Materials Dept., Mitsubishi Chemical[Open in a new window]
