- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Ion Exchange Resin Business Gr. Separation Materials Dept.
Weakly Acidic Cation Exchange ResinsDIAION™ series
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
Characteristics
[Close]
The weakly acidic cationic exchange resins have the chemical structures shown in the figures below with carboxylic acid groups (-COOH) as exchange groups. They show weak acidity like acetic acid, having the ability to exchange with bases such as NaOH and weak acid salts such as NaHCO3.
There are two kinds of chemical structures --- a methacrylic acid type and an acrylic acid type. This makes a difference for the degree of acidity of the exchange group. Because of this, the methacrylic acid type can be used at pH greater than about 5, while the acrylic acid type can be used at pH greater than about 4. Given this pH range restriction, use is restricted compared to a strongly acidic cation exchange resin. But as will be described later, the weakly acidic resin is easier to regenerate.
Weakly Acidic Cation Exchange Resin Chemical Structures
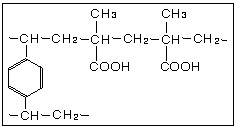
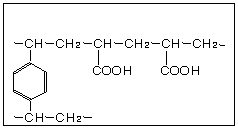
Since the carboxylic acid exchange group (-COOH) is driven toward the undissociated form in acidic solutions, the weakly acidic resin does not exchange with salts like NaCl and Na2SO4 in which a strong mineral acid would be formed. Thus equation (1) below shows the reverse reaction. Bases like NaOH and weak acid salts like NaHCO3 are exchangeable as shown in (2) and (3).
R-COOH + NaCl ← R-COONa + HCl (1)
R-COOH + NaOH → R-COONa + H2O (2)
R-COOH + NaHCO3 ⇔ R-COONa + H2O + CO2(3)
(R represents the ion exchange resin matrix.)
The adsorption strength (selectivity) of various ions on the weakly acidic cation exchange resin is generally analogous to that on the strongly acidic resin. Selectivity is higher for higher valence ions. However, the weakly acidic resin features very large selectivity for the hydrogen ion. This means that after the hydrogen ion is replaced by another cation, the resin can be easily regenerated --- returned to the R-COOH form --- using a chemical treatment (generally HCl or H2SO4 solutions). The required amount of the regeneration chemical is only slightly greater than the theoretical chemical equivalent for the weakly acidic resin.
Applications
[Close]
The acrylic acid-based weakly acidic cation exchange resin has a little higher acidity and is used for processing high carbonate hardness water. Combined with a strongly acidic cation exchange resin in a demineralization system, the used regenerant solution from the strongly acidic resin can be used to regenerate the weakly acidic resin for cost and material savings.
On the other hand, the methacrylic acid-based resin is less acidic and is not used much for water processing. It is used for antibiotic and amino acid purification.
Usage
Packed column or Batch processing
A disadvantage of the weakly acidic resin is a rapid volume change when going from the form with the H+ ion to a form with another ion. Since the resin may swell to nearly double its size, thorough precautions are required to prepare for higher fluid pressure drop across the column and to avoid damage to the column.
Lineup / Specifications
[Close]
Refer to the "ION EXCHANGE RESINS "[別窓表示]websites.
Inquiries Concerning Products
View the products of Separation Materials Dept., Mitsubishi Chemical[Open in a new window]
